BELEN
Beta-delayed Neutrons. The BELEN DetectorUnveiling the Secrets of Exotic Nuclei: Radioactive isotope facilities play a crucial role in exploring the properties of exotic nuclei, particularly those rich in neutrons. However, venturing into this neutron-rich territory presents a unique challenge beta-delayed neutrons. Beta-delayed neutrons and their significance: As the neutron-richness increases, the neutron separation energy (Sn) decreases, leading to a new decay mechanism: beta-delayed neutron emission. These "beta-delayed neutrons" (βn) are crucial for:
Enter BELEN: Pioneering Neutron Detection The BELEN (BEta-deLayEd Neutron detector) is a detector designed to measure beta-delayed neutron emission probabilities of nuclei of interest in nuclear technology and physics. Simple design, high efficiency: BELEN consists of a set of rings made of thermal neutron detectors (He-3) embedded in a high-density polyethylene (moderator) matrix. This design offers high detection efficiency within a predefined neutron energy range. A legacy of success: The BELEN concept has been used in numerous experiments at leading facilities like GSI (Germany) and IGISOL (Finland). Different versions, optimized for specific energy ranges, have been developed by UPC and the Experimental Nuclear Physics group of IFIC. These versions, utilize a digital electronic trigger-less data acquisition system (Gasific) for accurate measurements.
BELEN-20 neutron detector at IGISOL facility (University Jyväskylä, Finland)
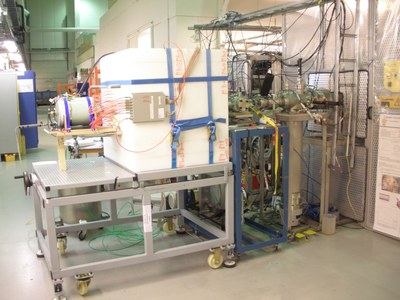
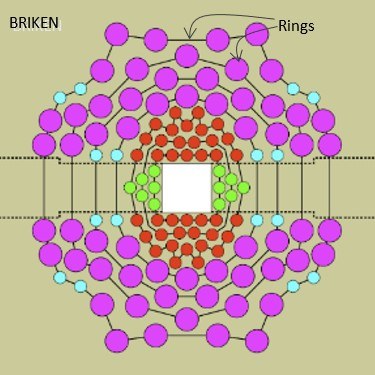
BELEN-48 neutron detector at IGISOL facility (University Jyväskylä, Finland) DAQ using Gasific (IFIC, Valencia) BRIKEN: The World's Most Efficient Neutron Detector Array Building upon BELEN's success, BRIKEN (BELEN for RIKEN) stands as the world's most efficient neutron detector array. This innovation boasts 140 He-3 tubes strategically arranged in a seven "pseudo-ring" geometry. BRIKEN has been instrumental in a long-lasting experimental campaign at RIKEN (2016-2021) and can even, to some extent, measure neutron energy spectra, a capability absent in previous BELEN iterations.
BRIKEN detector geometry
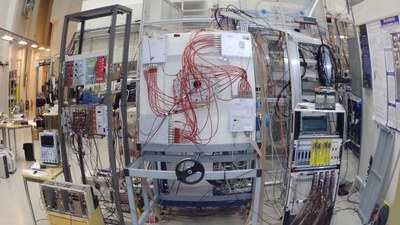
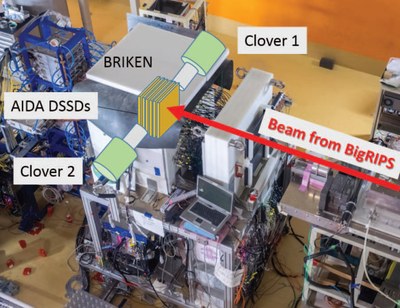
BRIKEN detector at RIKEN facilities (Japan) BRIKEN and AIDA detectors at RIKEN(Japan) The future: With the BELEN concept, we continue to push the boundaries of nuclear science, unveiling the secrets of exotic nuclei and contributing to advancements in nuclear structure, astrophysics, and reactor technology. While each BELEN ring can be approximated as a Bonner sphere, further development is ongoing to extract neutron energy information through advanced unfolding techniques. |


Share: